FAQ - Display and Topology
This article provides guidance on how setting up optimize and troubleshoot your PCoIP display issues.
FAQ – Questions
General
- What display resolutions can be supported?
- What display topologies are available?
- Which monitors will be used for the remote desktop?
- What is PCoIP Ultra and when should it be used?
- What is an accelerated display vs. an non-accelerated display?
- Do we attach monitors to both the client and the host?
Health Checks
- Client Display Health Check - Diagnostics and troubleshooting guide
- Host Display Health Check - Diagnostics and troubleshooting guide
Troubleshooting
- No Display: How to fix black, grey or a "No Source Signal" screen issue?
- Poor Display: How to fix displays with artifacts (blurry, dithering, pixelated, or flickering)
- Wrong Resolution: How to fix display resolution issues?
- Multiple Monitors: How to fix issues when attaching multiple monitors?
- DOT: Why do I see a yellow/blue/magenta dot on my display?
Turning Guidelines: Details on how to design and tune your PCoIP environment:
- PCoIP® Session Planning Guide
- HP Anyware Work-From-Home Rapid Response Guide
- Tuning PCoIP for high performance workloads
- How to tune PCoIP for bandwidth constrained Network?
Measuring Performance
FAQ – Answers
What display resolutions can be supported?
PCoIP supports resolutions from 600x800 SVGA up to and including 3840 x 2160 4K/UHD.What display topologies are available?
PCoIP clients can support configurations up to 4 monitors.The monitors can be arranged in a vertical line, a horizontal line, or as a 2×2 box display.
The monitors can be configured for any standard rotation (0°, 90°, 180°, or 270°).
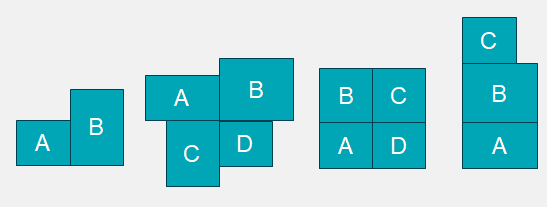
To ensure a valid topology, make sure that the following rules are followed when setting up your client topology:
- No more than 4 monitors.
- No display larger than 3840 x 2160 4K/UHD.
- No overlaps.
- No Gaps. At least one pixel of each display must abut at least one pixel of another display.
Diaram 2: Invalid topologies
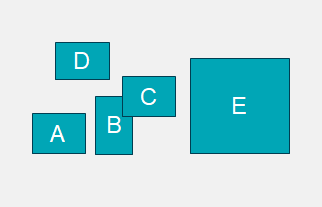
Which monitors will be used for the remote desktop?
When using a PCoIP software client, the monitors can be used either reserved for the remote desktop that is streamed to the client by the host or it can be used for local applications (FULL SCREEN mode) or the monitors can be shared with the remote desktop being presented in a window (WINDOWED mode).
Diagram 3: Full Screen Mode Topology Options:
In FULL SCREEN mode, client is able to use 1 monitor (any one) for a remote session. In this mode, all other monitors are used for local applications. Client is also able to use all monitors for a remote session. In this mode, no monitors are used for local applications.
Diagram 4: Windowed Mode Topology Options:

In WINDOWS mode, the client is able to have one window open to the remote host's desktop. All other windows on the desktop are served by the local client. The remote window window can be on any monitor and can be sized across monitors as well.
What is PCoIP Ultra and when should it be used?
“PCoIP Ultra™ represents our most advanced protocol enhancements yet, designed to meet the needs of the most demanding graphics-intensive applications while delivering the same lossless image quality and security our customers expect. Use PCoIP Ultra when you need to deliver 4K/UHD high frame rate content or want to use third party codecs, including H.264/HEVC.
What is an accelerated display vs. an non-accelerated display?
An accelerated PCoIP display is when a display adaptor on the agent is being served using a hardware assist, GPU. A non-accelerated PCoIP display is a display adaptor on the agent that is being served without a hardware assist GPU.
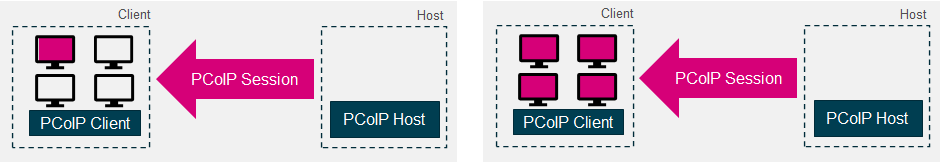
Can monitors be attached to both the client and the host?
Typically, we recommend that the host,is deployed as a headless server with no monitors attached. The desktop generated by the host is remoted to the PCoIP client and displayed on the monitors attached to the client.
Diagram 5: PCoIP Client with a Dual display topology connected to a headless host:
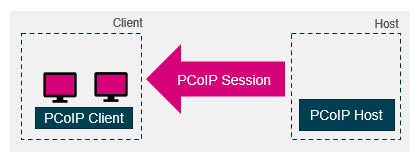
Alternatively, if both the host and client are configured with monitors. When the client establishes a remote session, both the client monitors and the host local monitors will be active and visible to bystanders during the remote session which may pose a local security risk. For more details on this configuration, consult the Teradici Work from Home Guide.
Diagram 6: Dual display topology connected to a host with 4 monitors (Deskside Mode)
No Display: How to fix black. grey or a "No Source Signal" screen issue?
Cause:
Black/Grey or "No source Signals" screens on your client monitors can be caused by:
- Cause #1: PCoIP client cannot detect the attached monitor
- Cause #2: Host Display adaptors may not be configured correctly
- Cause #3: Host Display adaptors may be configured to limit the resolution or topologies offered.
- Cause #4: Incorrect cabling or faulty cables when using a remote workstation card as a host.
- Cause #5: PCoIP client cannot support the topology/resolution requested by the host
Black screens on your host monitors can be caused by:
-
Cause #6: Client requested a topology/resolution that is incompatible with the host monitors.
Recommendations:
|
Black, Grey Screen Issues |
Remedy |
|---|---|
|
Cause #1: PCoIP client cannot detect the attached monitor
|
|
|
Cause #2: Host Display adaptors may not be using certified PCoIP display drivers
|
|
|
Cause #3: Host Display adaptors may be configured to limit the resolution or topologies offered
|
|
|
Cause #4: Incorrect cabling or faulty cables when using a remote workstation card as a host |
|
|
Cause #5: PCoIP client topology/resolution is invalid |
|
|
Cause #6: Client requested a topology/resolution that is incompatible with the host monitors |
|
Poor Display: How to fix displays with artifacts (blurry, dithering, pixelated or flickering)?
Cause:
- Cause #1: Blurry displays are caused by lack of available network bandwidth.
- Cause #2: Artifacts such as pixelation or screen tearing caused by dropped packets due to network issues or lack of CPU resources
Recommendations:
Checking the following items will solve most artifact issues:
|
Artifact Issues |
Remedy |
|---|---|
|
Cause #1: Blurry displays are caused by lack of available network bandwidth.
|
|
|
Cause #2: Artifacts such as pixelation or screen tearing caused by dropped packets due to network issues or lack of CPU resources
|
|
Wrong Resolution: how to fix display resolution issues?
Cause:
Display resolutions and topology setting are negotiated between the client and the host. The client will request specific resolutions for each monitor at session setup. A display resolution issues may be caused by:
- Cause #1: Incorrect resolution is currently configured on the PCoIP Client OS
- Cause #2: Host Display adaptors may not be using certified PCoIP display drivers
- Cause #3: Host Display adaptors may be configured to limit the resolution or topologies offered
- Cause #4: PCoIP client cannot support the topology/resolution requested by the host
Recommendations:
|
Wrong resolution |
Remedy |
|---|---|
|
Cause #1: Incorrect resolution is currently configured on the PCoIP Client OS
|
|
|
Cause #2: Host Display adaptors may not be using certified PCoIP display drivers
|
|
|
Cause #3: Host Display adaptors may be configured to limit the resolution or topologies offered
|
|
|
Cause #4: PCoIP client cannot support the topology/resolution requested by the host |
|
Multiple Monitors: How to fix issues with attaching multiple monitors?
Causes:
If additional monitors cannot be attached to the client, the cause may be:
- Cause #1: Client cannot detect the attached monitor.
- Cause #2: Host Display adaptors may not be using certified PCoIP display drivers
- Cause #3: Host is not capable of supporting the client topology
- Cause #4: Host has incorrect/faulty cabling sequence (Remote Workstation Card)
- Cause #5: Client not capable of full screen modes on 2 or 3 monitors with 4 monitors attached
Recommendations:
|
Wrong resolution |
Remedy |
|---|---|
|
Cause #1: Client cannot detect the attached monitor.
|
|
|
Cause #2: Host Display adaptors may not be using certified PCoIP display drivers
|
|
|
Cause #3: Host is not capable of supporting the client topology
|
|
|
Cause #4: Host has incorrect/faulty cabling sequence (Remote Workstation Card) |
DOT: Why do I see a yellow/blue/magenta dot on my display?
Causes:
- A yellow dot in the upper right hand side of the display indicates that the display is non-accelerated.
- A green dot in the upper right hand side of the display indicates that the display is accelerated
- A magenta dot in the lower left hand side of the display indicates that PCoIP is in ULTRA mode and GPU Optimization is enabled.
- A blue dot in the lower left hand side of the display indicates that PCoIP is in ULTRA mode and CPU optimization is enabled.
Recommendations:
-
If you see a yellow dot then your GPU is not activated likely due to an invalid driver or unsupported GPU.
-
The Magenta or Blue dot indicate that the system has been successfully setup to use ULTRA.
-
If you would like to disable or enable the dots, then consult the HP Anyware agent administration guide.
-